
Ancient Ayurveda Recipes for Healthy Living
by Vanita Dahia What did our ancestors eat? One ancient

by Vanita Dahia
 Heard of the gut-brain connection?
Heard of the gut-brain connection?
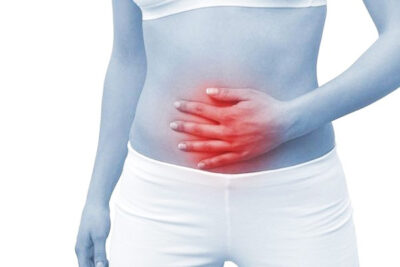
Stomach in a knot when depressed?
Changes in bowel habits when anxious or stressed?
Pains in the gut when worried?
The connection between the gut and the brain is gaining much repute within the published research. The value of the vagus nerve, the main highway between the gut and the brain has now been shown to prove extremely valuable in management of mental health conditions.
The gut microbiota is a compilation of all the bugs, whether beneficial (commensal) or damaging (pathogenic) control the microbial ecology and immunity within the gut. If the ecology is out of balance, the capacity for the gut to manufacture essential happy and sad brain chemicals called neurotransmitters is impaired.
Happy brain chemicals or neurotransmitters are predominantly synthesised in the gut.
The vagus nerve connects the gut lining to the brain stem. Research has shown that specific probiotic and prebiotic loading of the gut has the capacity to lower elevated stress levels or cortisol levels and in turn assist in management of depression related despair.
In a study by Panyko, 2015, a probiotic called lactobacillus Rhamnosus has been shown to reduce anxiety and depression by maintaining GABA levels and stressed induced corticosteroid levels. Interestingly enough, when the vagus nerve was severed behaviour remained unchanged after treatment with lactobacillus Rhamnosus.
As the research and study on the therapeutic value of probiotics have increased, we find that targeted probiotic therapy to optimise the microbial ecology in the gut is a valuable construct within the treatment of mental health.
The vagus nerve is the main nerve connecting the gut to the brain. Stimulating the vagus nerve has shown to be beneficial in stimulating electrical impulses from the brain to organ systems in the body. Therapeutic vagal stimulation is used therapeutically to treat epilepsy, Alzheimers and severe cases of depression. Conventional vagus nerve stimulation involves surgically implantation of a device under the skin.
The vagus nerve can help reduce pain, stimulate appetite, and regulate hunger through hormones. For example Ghrelin, and appetite regulating hormone increases hunger by stimulating the vagus nerve signal from the brain to the gut.
The vagus nerve is predominantly responsible for the mind body connection and works by:
• controls anxiety and depression
• increases stomach acidity, digestive juices secretion and gut flow
• increases the release of histamine by the stomach cells
• controls heart rate and blood pressure
• controls blood glucose
• helps release bile from the gallbladder to get rid of toxins and break down fat
• promotes kidney function by improving blood filtration and excreting minerals
• controls appetite satiety hormones regulating hunger and satiety
Take a cold shower – the body reacts to the cold by stimulating the flight or fright/sympathetic nervous system
Sing or Chant – singing on top of your voice, humming, chanting, controlled breathing techniques, energizes and activates the sympathetic nervous system and the vagus nerve.
Yoga, tai chi, jiggling, Pilates, laughter clubs, prayer, massage, meditation has the capacity to increase vagus nerve activity and support the parasympathetic nervous system.
Social interaction with friends and family have shown to improve vagal function and heart rate variability.
Intermittent fasting or reducing calories not only increases heart rate variability, but also assists in regulating metabolism which is mediated by the vagus nerve.
Adequate and fulfilled sleep, a reparative and restorative necessity is required for optimal vagal function.
Yoga exercises involving gargling, extending the tongue together with controlled breathing exercises will assist in contracting muscles which activates the vagus nerve is and stimulates the gastrointestinal tract.
Pulsed magnetic stimulator (PEMF) have been shown to increase heart rate variability.
Acetyl Choline (Ach) is the main vagal neurotransmitter. It assists in reducing inflammatory cytokines and improving memory and focus.
Choline, an amino acid is needed to make the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is required for cognitive and muscular function. Choline is important for many cellular pathways such as the making of Acetylcholine. It plays a key role in cognitive function, cardiovascular function, and infant development.
Dietary sources of Choline includes eggs, beef liver, grass fed diary and cruciferous vegetables.
Probiotic supplementation have shown to improve stress induced cortisol levels and positive changes in GABA levels which are mediated by the vagus nerve.
Test your neurotransmitters.
Contact us for further information.

by Vanita Dahia What did our ancestors eat? One ancient

Have you ever heard of anyone preventing their memory decline
How to Stop Indigestion and Acid Reflux by Vanita Dahia

Copyright © Vanita Dahia 2026. All rights reserved.